INTRODUCTION TO GEOLOGY
Geology (in Greek, Geo means Earth, Logos means Science) is a branch of science dealing with the study of the Earth. It is also known as earth science. The study of the earth comprises of the whole earth, its origin, structure, composition and history (including the development of life) and the nature of the processes. The word was first used in 1778 in the work of Jean Andrea de Luc (a Swiss-born scientist who lived at Windsor for much of his life as adviser to Queen Charlotte) and at much the same time in the work of Swiss Chemist, S.B. Saucer.
Geology is a fascinating subject.
Geology feels the pulse of the earth.
Geologists contribute their part to the nation through the discovery of new deposits of rocks and minerals of economic value.
A student should know what lies beneath the crust and how long back the earth came into existence.
DIFFERENT BRANCHES OF GEOLOGY
(i) Physical Geology (ix) Economic Geology
(ii) Crystallography (x) Mining Geology
(iii) Mineralogy (xi) Civil Engineering Geology
(iv) Petrology (xii) Hydrology
(v) Structural Geology (xiii) Indian Geology
(vi) Stratigraphy (xiv) Resources Engineering
(vii) Paleontology (xv) Photo Geology
(viii) Historical Geology
(i) Physical Geology
As a branch of geology, it deals with the “various processes of physical agents such as wind, water, glaciers and sea waves”, run on these agents go on modifying the surface of the earth continuously.
Physical geology includes the study of Erosion, Transportation and Deposition (ETD).
The study of physical geology plays a vital role in civil engineering thus:
(a) It reveals constructive and destructive processes of physical agents at a particular site.
(b) It helps in selecting a suitable site for different types of project to be under taken after studying the effects of physical agents which go on modifying the surface of the earth physically, chemically and mechanically.
(ii) Crystallography
As a branch of geology, it deals with ‘the study of crystals’. A crystal is a regular polyhedral form bounded by smooth surfaces. The study of crystallography is not much important to civil engineering, but to recognize the minerals the study of crystallography is necessary.
(iii) Mineralogy
As a branch of geology, it deals with ‘the study of minerals’. A mineral may be defined as a naturally occurring, homogeneous solid, inorganically formed, having a definite chemical composition and ordered atomic arrangement. The study of mineralogy is most important.
(a) For a civil engineering student to identify the rocks.
(b) In industries such as cement, iron and steel, fertilizers, glass industry and so on.
(c) In the production of atomic energy.
(iv) Petrology
As a branch of geology it deals with ‘the study of rocks’. A rock is defined as “the aggregation of minerals found in the earth’s crust”.
The study of petrology is most important for a civil engineer, in the selection of suitable rocks for building stones, road metals, etc.
(v) Structural Geology
As a branch of geology, it deals with ‘the study of structures found in rocks’. It is also known as tectonic geology or simply tectonics.Structural geology is an arrangement of rocks and plays an important role in civil engineering in the selection of suitable sites for all types of projects such as dams, tunnels, multi storied buildings, etc.
(vi) Stratigraphy
As a branch of geology it deals with ‘the study of stratified rocks and their correlation’.
(vii) Paleontology
As a branch of geology, it deals with ‘the study of fossils’ and the ancient remains of plants and animals are referred to as fossils. Fossils are useful in the study of evolution and migration of animals and plants through ages, ancient geography and climate of an area.
(viii) Historical Geology
As a branch of geology, it includes “the study of both stratigraphy and paleontology”. Its use in civil engineering is to know about the land and seas, the climate and the life of early times upon the earth.
(ix) Economic Geology
As a branch of Geology, it deals with “the study of minerals, rocks and materials of economic importance like coal and petroleum”.
(x) Mining Geology
As a branch of geology, it deals with “the study of application of geology to mining engineering in such a way that the selection of suitable sites for quarrying and mines can be determined”.
(xi) Civil Engineering Geology
As a branch of geology, it deals with “all the geological problems that arise in the field of civil engineering along with suitable treatments”. Thus, it includes the construction of dams, tunnels, mountain roads, building stones and road metals.
(xii) Hydrology
As a branch of geology, it deals with “the studies of both quality and quantity of water that are present in the rocks in different states”(Conditions). Moreover, it includes:
(a) Atmospheric water,
(b) Surface water, and
(c) Underground water.
(xiii) Indian Geology
As a branch of geology, it deals with “the study of our motherland in connection with the coal/petroleum, physoigraphy, stratigraphy and economic mineral of India”.
(xiv) Resources Engineering
As a branch of geology deals with “the study of water, land, solar energy, minerals, forests, etc. fulfill the human wants”.
(xv) Photo Geology
As a branch of geology deals with “the study of aerial photographs”.
RELATIONSHIP OF GEOLOGY WITH OTHER BRANCHES OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
In order to carry out civil engineering projects safely and successfully, geology should be related to the other branches of bordering sciences as described as follows:
1. Geochemistry
As a branch of science, it deals with geology in such a way that it concerns with the abundance and distribution of various elements and compounds in the earth.
2. Geophysics
As a branch of science, it is related with geology in such a way that it concerns with the constitution of the earth and the nature of the physical forces operating on with in the earth.
3. Geo Hydrology
As a branch of science, it is related with geology in setting of ground water. In other words, Geo hydrology is an “interaction between Geology and Hydrology”.
4. Rock Mechanics
As a branch of science, it is related with geology in dealing with the behaviour of rocks that is subjected to static and dynamic loads (force fields).
5. Mining Engineering
Geology is related to mining engineering in dealing with the formation and distribution of economic minerals and response to fracturing processes. With out the knowledge of structural features of rock masses and mode of occurrence and mineral deposits, a mining engineer cannot determine the method of mining.
6. Civil Engineering
Before constructing roads, bridges, tunnels, tanks, reservoirs and buildings, selection of site is important from the viewpoint of stability of foundation and availability of construction materials. Geology of area is important and rock-forming region, their physical nature, permeability, faults, joints, etc. Thus, geology is related to civil engineering in construction jobs with economy and success.
IMPORTANCE OF GEOLOGY FOR CIVIL ENGINEERING
The role of geology in civil engineering may be briefly outlined as follows:
1. Geology provides a systematic knowledge of construction materials, their structure and properties.
2. The knowledge of Erosion, Transportation and Deposition (ETD) by surface water helps in soil conservation, river control, coastal and harbour works.
3. The knowledge about the nature of the rocks is very necessary in tunneling, constructing roads and in determining the stability of cuts and slopes. Thus, geology helps in civil engineering.
4. The foundation problems of dams, bridges and buildings are directly related with geology of the area where they are to be built.
5. The knowledge of ground water is necessary in connection with excavation works, water supply, irrigation and many other purposes.
6. Geological maps and sections help considerably in planning many engineering projects.
7. If the geological features like faults, joints, beds, folds, solution channels are found, they have to be suitably treated. Hence, the stability of the structure is greatly increased.
8. Pre-geological survey of the area concerned reduces the cost of engineering work.
SCOPE OF GEOLOGY
Engineering Geology:
A well established interdisciplinary branch of Science and Engineering has a scope in different fields as outlined below:
(a) In Civil Engineering:
Geology provides necessary information about the site of construction materials used in the construction of buildings, dams, tunnels, tanks, reservoirs, highways and bridges. Geological information is most important in planning phase (stage), design phase and construction phase of an engineering project.
(b) In Mining Engineering:
Geology is useful to know the method of mining of rock and mineral deposits on earth’s surface and subsurface.
(c) In Ground Water:
Resources development geology is applied in various aspects of resources and supply, storage, filling up of reservoirs, pollution disposal and contaminated water disposal.
(d) Land pollution.
(e) Nuclear explosion.
(f) Oceanography.
(g) Space exploration.
In each of the above-mentioned fields Geology has to deal with an integral part of the earth.
EARTH AS A PLANET
The earth is a planet belonging to the solar system of the Milky Way Galaxy, with a natural satellite, the moon. It is the third planet from the Sun. The planet on which we live is called the earth. There is a lotof disagreement between the scientists regarding the shape of the earth. In recent times a new phrase being used is that the earth is like a GEOID (Greek, GEO = earth, OID = like) i.e., our planet is like the earth. They believe that the interior of the earth is shrinking day by day. This shrinkage may be either due to loss of heat or reorganization of molecules under enormous pressure and high temperature. It is thus obvious that the outer portion must shorten its circumference to adjust the shrunken interior.
Table 1.1 Chart of the diameter and the area of the earth, according to the present state of knowledge about it.
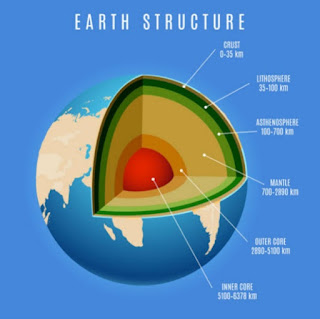
STRUCTURES AND COMPOSITION OF EARTH





Very simple and good
ReplyDeletePerfect
ReplyDeleteThank you
ReplyDeletethanks sir
ReplyDelete